Argentina’s Economic Evolution and Mining Investment Guide
Opportunities and Reforms under President Javier Milei
Historical Context: Argentina’s Economic Journey
Argentina’s economy has swung between periods of prosperity and crisis. Once a global agricultural powerhouse, heavy state intervention, protectionism, and chronic inflation eroded competitiveness throughout the late 20th and early 21st centuries. Repeated currency crises, debt defaults, and populist policies led to investor skepticism and capital flight. By 2022, Argentina faced triple-digit inflation, dwindling reserves, and a fractured social contract—a backdrop that set the stage for radical change.
The Ascent of Javier Milei: Background and Ideology
Javier Milei, an economist and outspoken libertarian, rose from political outsider to president in 2023 on promises of “shock therapy”—drastic market liberalization, fiscal discipline, and a smaller state. His platform resonated with voters disillusioned by stagnation and government overreach. Milei’s administration is characterized by bold, sometimes contentious reforms aimed at restoring investor confidence and unleashing Argentina’s economic potential.
Milei’s Economic Reforms: Shock Therapy and Fiscal Measures
Since taking office, Milei has implemented sweeping changes:
Fiscal Austerity: Deep cuts to public spending, subsidy reductions, and aggressive deficit reduction.
Deregulation: Removal of price controls, labor market flexibility, and privatization of state-owned enterprises.
Currency Controls: Gradual easing of FX restrictions, with steps toward dollarization and integration of USD transactions.
Tax Reform: Lower corporate rates, simplification of tax codes, and incentives for foreign investment.
Mining Incentives: Special regimes to attract capital and technology to the sector.
These reforms have generated optimism among investors, but also social friction as layoffs and subsidy cuts impact vulnerable populations.
Recent Developments (September–October 2025)
Economic Stagnation Signals: Despite reforms, GDP growth plateaued in Q3 2025, with persistent unemployment and sluggish consumer demand. Inflation moderated but remains above 20% annually.
U.S. Bailout Offer: On September 15, 2025, the U.S. Treasury proposed a $10 billion emergency credit line to stabilize Argentina’s reserves, contingent on further fiscal discipline and anti-corruption measures. Negotiations are ongoing, with mixed political reception.
Political Setbacks: Milei’s coalition lost key votes in Congress, stalling additional deregulation bills and sparking protests over public sector layoffs and pension reforms.
Mining Investment Milestones: Major new lithium and copper projects were greenlit in Jujuy and San Juan provinces, with total commitments exceeding $5 billion. Export volumes hit record highs, aided by the elimination of export duties.
Government Downsizing: Cabinet and Agency Reductions
Milei’s administration has aggressively reduced the size of government—merging ministries, closing redundant agencies, and laying off thousands of public employees. While this has improved fiscal metrics and sent positive signals to investors, it has also fueled social unrest and resistance from labor unions and opposition parties.
Mining Sector Renewal: Incentives and Major Projects
The mining sector is central to Milei’s growth agenda. Key reforms include:
RIGI Incentives: The “Regimen de Incentivo para Grandes Inversiones” (RIGI) offers tax holidays, streamlined permitting, and protected FX access for large projects.
Export Duty Elimination: All export taxes on mining products were lifted in September 2025, boosting competitiveness.
Capital Controls: Restrictions on profit repatriation and cross-border payments have been eased, allowing foreign investors greater flexibility.
Major Projects: Notable investments in lithium (Jujuy, Catamarca), copper (San Juan), and gold (Santa Cruz) have drawn global players, including U.S., Canadian, and Australian firms.
Environmental Considerations: New regulations mandate strict ESG compliance, water management, and community engagement, aligning Argentina with international standards.
Mining Taxation and Export Regimes
Mining operations benefit from fiscal stability agreements, with fixed royalty rates (3%–5%), lower corporate taxes (25%), and streamlined export procedures. The RIGI regime guarantees stable tax treatment for up to 30 years, shielding investors from abrupt policy shifts. Export proceeds can be held offshore or remitted in USD, providing flexibility.
General Tax Reform and Deregulation
Beyond mining, Argentina has enacted broad pro-business reforms:
Corporate tax rate cut from 35% to 25%.
Simplification of VAT and payroll taxes.
Reduced red tape for company registration and foreign ownership.
Digitalization of tax filing and payment processes.
These measures have improved the World Bank’s “Ease of Doing Business” rankings, although enforcement and local bureaucracy remain uneven.
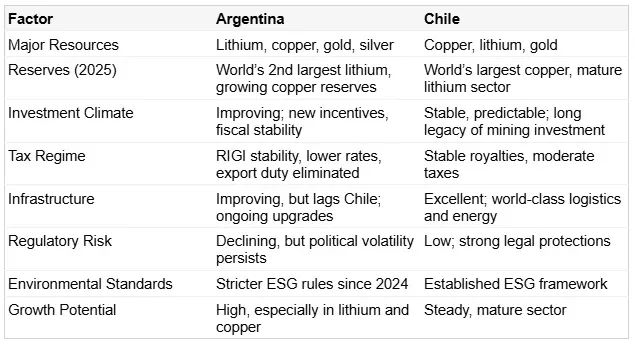
Argentina vs. Chile: Comparative Mining Sector Analysis
Enabling Factors and Remaining Challenges;
Enabling Factors: Abundant resources, major reforms, improving regulatory environment, and strong global demand for battery metals.
Challenges: Infrastructure gaps (roads, rail, energy), social unrest from job losses, lingering political volatility, and uneven implementation of reforms.
Risk Mitigation: Investors should monitor political developments, build local partnerships, and prioritize ESG compliance.
Banking System Reforms in Argentina: Focus on USD Integration
Under President Javier Milei, Argentina has undergone significant banking and currency reforms since late 2023, aimed at dismantling decades of capital controls and fostering a more open, market-driven financial system. A cornerstone of these changes is the liberalization of USD transactions, which addresses the country’s historical reliance on the U.S. dollar as a store of value amid chronic inflation and peso devaluation. The most pivotal reform occurred on April 14, 2025, when the government lifted most currency controls—known as the cepo cambiario—eliminating restrictions on foreign exchange purchases, profit repatriation, and payment timelines for imports. This allows individuals and businesses to freely buy USD without limits or delays, and companies can now access foreign currency immediately upon shipment arrival (previously a 30-day wait). The administration plans to fully eliminate remaining controls by the end of 2025, supported by a $20 billion IMF agreement. Additionally, Milei launched a campaign in June 2025 urging Argentines to deposit an estimated $271 billion in hoarded “mattress dollars” (hidden USD cash) into banks, backed by a tax amnesty and a “Fiscal Presumption of Innocence” bill that reduces reporting requirements and shields depositors from penalties. These reforms integrate USD into the formal economy without full dollarization, stabilizing the peso while enhancing USD accessibility.
Opening a Bank Account in Argentina as a U.S. Citizen
U.S. citizens, including non-residents, can open bank accounts in Argentina relatively straightforwardly, thanks to these reforms and the Central Bank of Argentina’s (BCRA) encouragement of foreigner access. A passport suffices for basic savings accounts—though some banks may request additional proof for enhanced services. The process typically takes 1-2 weeks and must often be done in person at a branch, as online options are limited for foreigners.
Key Requirements:
Identification: Valid U.S. passport (primary document; no DNI needed).
Tax ID: CUIL (for employees) or CUIT (for self-employed/business)—easy to obtain online via AFIP (Argentina’s tax authority) using your passport.
Proof of Address: Utility bill, rental agreement, or notarized landlord letter (can be from the U.S. or Argentina).
Proof of Income: Recent payslip, bank statement, or employment contract.
Other: Completed application form; sometimes a local reference or visa (e.g., tourist or Rentista visa for easier approval). U.S. citizens must comply with FATCA (Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act), meaning banks report account details to the IRS.
Recommended Banks for Foreigners:
Banco Nación Argentina (BNA), Banco Macro, Santander Río, HSBC Argentina, or Banco Patagonia— all offer English support and international services.
Step-by-Step Process:
Gather documents and select a bank based on needs (e.g., proximity, fees).
Schedule an appointment via the bank’s website or visit a branch.
Submit documents for verification and sign the agreement.
Make an initial deposit (often minimal, e.g., ARS 1,000 or USD 100).
Receive account details, debit card, and online banking setup.
Post-reform, these accounts now support unrestricted USD inflows/outflows, making it simpler for U.S. citizens to fund via wire transfers without exchange hurdles.
Saving in USD or Pesos
Argentine banks offer both peso (ARS) and USD-denominated savings and fixed-term deposit accounts. You can choose based on risk tolerance:
USD Accounts: Fully available post-April 2025 reforms. These are ideal for stability, as USD protects against peso volatility. Options include savings accounts (low/no interest) or fixed-term deposits (e.g., 30-365 days, minimum USD 500 at banks like Santander). Current rates are modest at around 0.97% per annum (as of March 2025), but transfers are free and repatriation unrestricted. Deposits can be made via international wires or cash (encouraged under Milei’s campaign).
Peso (ARS) Accounts: Easier to open (free for balances under ARS 312,500 and transactions below ARS 50,000/month). These earn higher interest—up to 47% annually (August 2025)—but expose you to inflation (currently ~3% monthly, down from 25% in 2023) and devaluation risks. Best for short-term local spending.
You can hold both currencies in the same account or separate ones, with seamless conversions at market rates.
Advantages for U.S. Citizens
These reforms offer U.S. citizens—whether expats, investors, or visitors—several perks in an emerging market context:
Currency Stability and Hedging: Save in USD to avoid peso erosion, with easy deposits of “mattress dollars” or wires. This is crucial in a high-inflation environment, providing a safe haven similar to U.S. banks but with local convenience.
Investment Access: Unrestricted profit repatriation opens doors to real estate, mining, or stocks via local brokerage tied to accounts. FATCA ensures IRS compliance, avoiding penalties.
Low Barriers and Costs: No residency needed; minimal fees (e.g., free peso savings under limits) and debit cards for daily use. High peso yields (if risk-tolerant) beat U.S. rates (~4-5% on savings).
Lifestyle/Expats Benefits: For retirees or digital nomads on visas, it simplifies remittances and payments, with growing English-friendly digital banking.
Overall, it’s a low-risk entry to diversify holdings in a reforming economy, potentially yielding better returns than pure U.S. options amid Argentina’s projected 5.5% GDP growth in 2025.
Advantages to the Argentine Economy
The reforms supercharge economic recovery by channeling idle capital into productive use:
Boosted Reserves and Liquidity: Depositing hoarded USD adds billions to bank reserves, stabilizing the peso (potentially appreciating from 1,180 to 1,000 ARS/USD) and supporting IMF-backed growth forecasts of 5.5% in 2025.
Attracts Foreign Investment: Free USD access draws U.S./global capital (e.g., via the $20B IMF deal), funding infrastructure and exports while reducing default risks.
Inflation Control and Trust: Formalizing “mattress dollars” curbs shadow economy distortions, sustains budget surpluses, and rebuilds confidence—poverty fell to 31.6% in H1 2025.
Broader Growth: Enhances trade (no import delays), spurs job creation in finance/tech, and positions Argentina as a USD-friendly hub in Latin America, countering Chinese influence.
While challenges like recent peso volatility persist, these changes mark a shift from isolation to integration, benefiting both locals and international players like U.S. citizens.
Update (Oct. 26.2025) Argentina’s midterm legislative elections on October 26, 2025, delivered a seismic win for President Javier Milei’s libertarian powerhouse, La Libertad Avanza, which surged to over 41% of the vote—crushing the opposition and clinching key seats in the Chamber of Deputies and Senate to fortify his razor-thin congressional edge. Riding a wave of nascent economic recovery and a hefty $40 billion U.S. bailout lifeline, Milei now wields a beefed-up mandate to turbocharge his shock-therapy agenda: gutting red tape, offloading state-owned behemoths, and fast-tracking dollarization to tame the peso’s wild ride. It’s full throttle on a libertarian revolution, even as inflation’s embers smolder and social fault lines strain under austerity’s bite—but with investor confidence soaring and growth projections brightening, this triumph sets the stage for a revitalized economy, drawing in foreign capital and steering Argentina toward long-term stability and prosperity.
Argentina, long recognized for its rich natural resources and turbulent economic history, is undergoing a profound transformation under President Javier Milei. This guide provides global investors, expats, and analysts with an authoritative, optimistic, and objective analysis of Argentina’s evolving investment landscape—focusing on recent reforms, mining sector incentives, tax and banking changes, and practical advice for U.S. citizens considering investment or banking in the country. Special emphasis is given to updates from September 1 to October 6, 2025, including economic stagnation signals, U.S. bailout negotiations, political developments, and major mining milestones.
Conclusion: A New Era for Argentina and Global Mining
Argentina’s economic journey is one of transformation—from early 20th-century prosperity to a turbulent century of intervention and decline, and now to a period of radical market liberalization. Under President Milei, sweeping reforms in mining, taxation, and fiscal policy have redefined the investment landscape. Despite ongoing challenges, including currency pressures and political resistance, Argentina’s abundant resources, pro-investment framework, and openness to global capital—supported by U.S. backing—make it a premier destination for investment in 2025 and beyond. For those prepared to navigate the risks and seize emerging opportunities, now is the time to engage with Argentina’s mining renaissance.
Upgrade to paid and unlock the companies we love with handpicked mining companies, energy plays and much more. With full breakdown and why they are great companies. Answering the unknown questions before they become answers.